Relative Clauses Meaning
Relative Clauses are also known as Adjective Clauses.
A relative clause does the job of an adjective. Check the following.
| “A girl” | “girl” is a noun |
| “A beautiful girl” | “beautiful” is an adjective |
An adjective describes a noun.
A clause is a group of words with a subject and predicate and gives a meaning. A clause can be considered a part of a complex or compound sentence. Therefore, a clause is always considered second to a sentence.
I helped a girl whose leg was injured.
A sentences with two clauses.
| I helped a girl | Main Clause |
| Whose leg was injured | Relative Clause |
In the above example, you can see a Complex sentence where there is a main clause and a relative clause. The main clause is provided with further information by the relative clause.
“Whose leg was injured” here is a group of words which describes the “girl” introduced in the main clause; “I helped a girl”.
This clause “whose leg was injured” provides further information to the main clause. This clause relates and supports to the main clause. Hence, is called “relative Clause”.
Thus, a relative clause describes a noun or a noun phrase and acts as a modifier. Accordingly, the function of an adjective and the adjective clause is same but the size of the unit is different.
| An Adjective | = A word that describes a noun |
| A relative Clause | = A group of words (with a subject and predicate) that describes a noun. |
Let’s take a look at a conversation for an example.
Your friend says : The man came to see me.
Here, you will wonder, “who was this man?”
Instead, if your friend had said the following, you would have understood better.
“The man who met me at the party came to see me.”
| The man came to see me. | - Main Clause |
| Who met me a the party | - Relative Clause which further describes the word “man” |
Let’s take a look at a different sentence now.
The house which was constructed with low quality material did not last long.
| The house did not last long | - Main Clause |
| Which was constructed with low quality material | - Relative Clause which further describes the word “house” |
Let’s say, you happen to hear a comment “The house did not last long.” And you wonder which house. The relative clause in the sentence provides you with the required information here.
Relative Pronouns
| Relative Pronouns | = who, whose, whom, which, that |
A relative pronoun does the work of a conjunction. It joins the main clause with the relative clause.
Let’s take a look at the following examples and identify the relative pronouns.
I helped a girl whose leg was injured.
The man who met me at the party came to see me.
The house which was constructed with low quality material did not last long.
Consider the function of “whose”, “who” and “Which” in the above examples. The relative pronouns introduce the relative clause and provide direct reference to the noun which is being described.
On the other hand, the relative pronoun poses the question that is being answered by the relative clause which follows it.
I helped a girl whose leg was injured.
Whose - refers to ‘a girl”
The man who met me at the party came to see me.
Who – refers to “the man”
The house which was constructed with low quality material did not last long.
Which – refers to “the house”
The relative pronouns help combine the two independent clauses together in order to provide more information.
When choosing the accurate relative pronoun to match the noun referred to, we need to consider the function of the noun in the particular main clause. (Whether it functions as the Subject, Object or in the Possessive form) Further, we need to see whether the noun refers to a “person” or a “thing”.
Proper usage of relative pronouns can be explained as follows.
Relative Pronouns according to usage
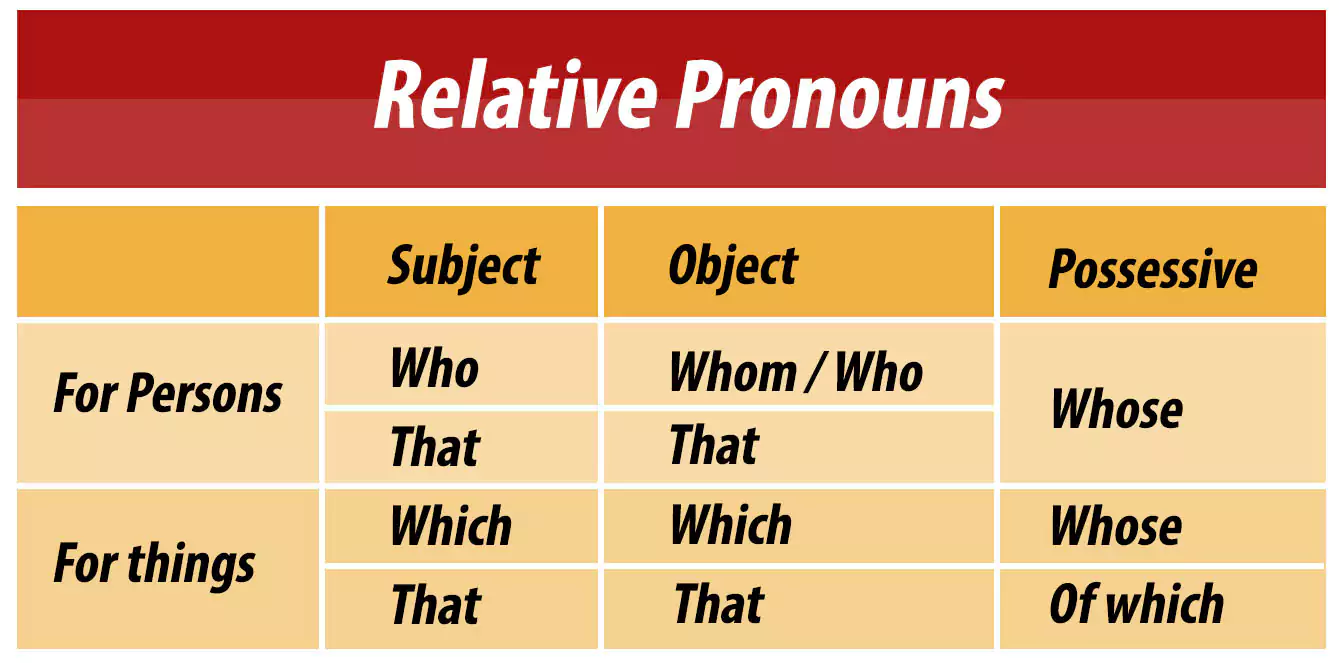
However, it is noteworthy that there are exceptions to these norms based on different contexts.
Let’s discuss the usage with reference to the following examples.
I helped a girl whose leg was injured.
“A girl” here is described using something she possesses. Therefore, we use the relative pronoun Whose
The man who met me at the party came to see me.
“The man” here represents the “Subject” of the main clause. It is also “a person”. Therefore we use Who .
The house which was constructed with low quality material did not last long.
“The house” here represents the “Subject” of the main clause. But it is “a thing”. Therefore we use which .
We can also substitute “which” with “that” often in conversational language, depending on the situation.
Practical Usage of Relative Clauses :-
- Help combine two related clauses into one sentence.
- Help write sentences condensed with a lot of information.
- Help write complex sentences.
RELATED POSTS
Hello!
I'm here to guide you
Learn English easy way, with simple clarifications along with suitable examples. Good luck on your new journey !
Explanations
Popular
Advanced English
Spoken English
Explore Poems
Business English

